Gameful learning is a pedagogical approach that draws inspiration from successful games. It involves analysing the mechanics and principles that make games engaging and then applying these insights to the learning environment. This approach, as highlighted in Klippe’s e-learning curriculum development principles, plays a vital role in fostering intrinsic motivation among learners. Below, we’ll explore the theories behind gameful learning and how to effectively implement them in the development of our learning materials.
Gameful Learning – The Key in Motivating Learners
At the core of gameful learning lies the integration of gaming logic and techniques into the learning process itself, rather than merely incorporating games or playful tasks. It’s essential to acknowledge the broader concept of gamification within this context, which entails utilizing various games and game elements in non-game aspects of life. While gameful learning and gamification share common ground, it’s important to distinguish between them within the realm of e-learning.
Gamification
Gameful Learning
Gamification
The curriculum has playful elements, such as virtual trophies as rewards.
Gameful Learning
The principle of playful learning is applied already in the curriculum design phase. Features like a scoring system, instant feedback, and transparency.
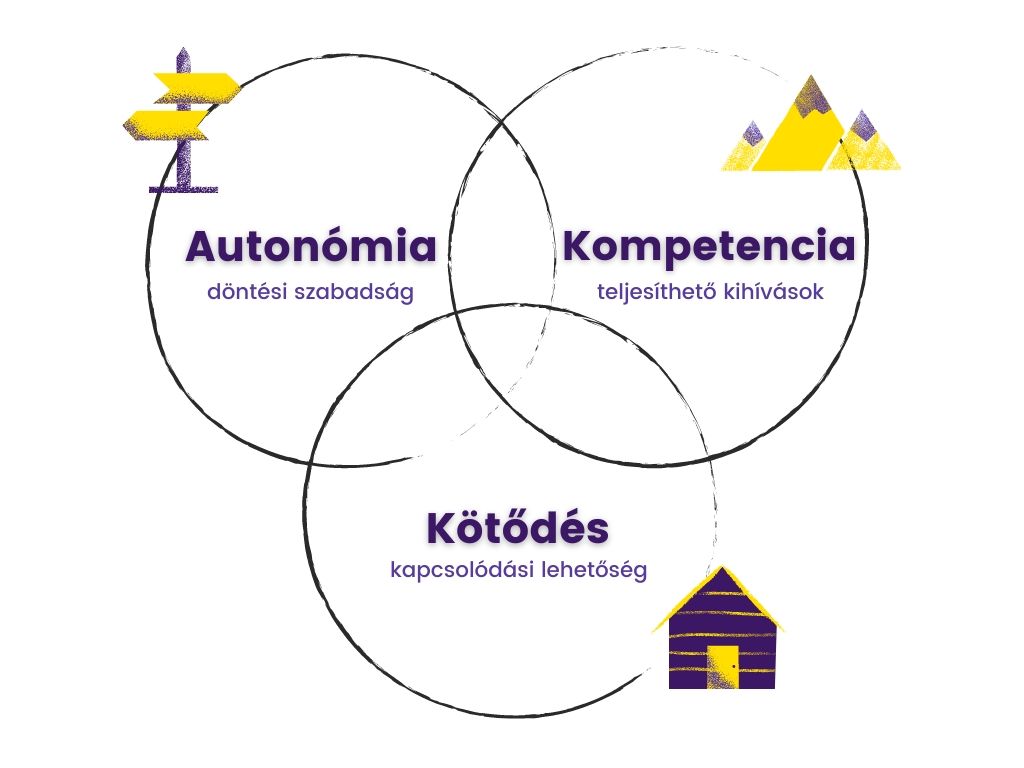
Self-Determination Theory – The Power of Intrinsic Motivation
At the core of captivating learning experiences lies the Self-determination Theory by Deci and Ryan. This theory underscores three vital components essential for fostering self-motivation: autonomy, competence, and connection.
Autonomy empowers learners to chart their own course, granting them the freedom to choose their path. Competence thrives in environments where challenges are just right – neither too easy nor too difficult – allowing learners to conquer tasks with a sense of accomplishment. Connection, on the other hand, bridges the gap between learners and educators, fostering a sense of belonging and collaboration.
Consider Sudoku: players select which puzzle to tackle and devise their own strategies for success. As they overcome challenges, a sense of competence blossoms, both fuelling their motivation further and allowing them to connect, sharing their experiences with fellow players and educators alike.
Flow – Joyful Learning
Mihály Csíkszentmihályi, the Hungarian-American psychologist credited with pioneering the concept of flow, is celebrated as a sage in the field. In essence, his expansive theory encapsulates a simple truth: within the flow state, action flows effortlessly, imbued with a natural sense of joy and ease. It’s the sweet spot where our motivation to excel thrives. Achieving this state demands several key elements: clear goals, constructive feedback, and unwavering focus.
At the heart of the flow theory lies a fundamental principle akin to the Self-determination Theory: the delicate equilibrium between our abilities and the challenges we undertake. This ensures that tasks neither bore us (when too easy) nor overwhelm us with anxiety (when too difficult).

Curriculum Development Guidelines
Our team members have been involved in e-learning curriculum development for many years. We’ve helped cashiers and bank employees master their new internal software solutions, insurance company colleagues to ace compliance trainings, employees of a multinational company to learn a new product, and many more. After numerous diverse projects and extensive experiences, we’ve distilled invaluable professional guidelines into 6+1 points.
Read more!Growth Mindset – Any Knowledge is Learnable
The concept of a growth mindset is closely linked with the work of American psychologist Carol S. Dweck. She proposes that everyone has the potential to enhance their learning and problem-solving capacities. Dweck divides people into two categories based on how they respond to setbacks: those with a fixed mindset and those with a growth mindset. Individuals with a fixed mindset view their abilities, intelligence, and talents as innate and unchangeable traits. In contrast, those with a growth mindset believe that with sufficient effort, all skills can be honed and knowledge can be acquired. Dweck’s theory is thoroughly explored in her book “Mindset: The New Psychology of Success“, published in 2006.
Achievement Goal Theory, Mastery Orientation – Motivation and Learning Goals
The Achievement Goal Theory delves into the concept of learning motivation, placing emphasis on understanding the diverse goals learners pursue. Motivations vary greatly among individuals: some are fuelled by ego, others by comparison to peers, and some simply strive to avoid failure. The Achievement Goal Theory identifies two primary types of goals, alongside numerous other intricate goal structures. At its core are mastery goals and performance goals. Those with a mastery orientation focus inward, seeking understanding, skill acquisition, and self-assess their progress. Conversely, individuals with a performance goal orientation prioritize surpassing others, showcasing individual abilities, and measuring success against external standards or peers.
“Picture your brain forming new connections as you meet the challenge and learn. Keep on going.” – Carol Dweck
Having Motivated Learners (Not Only) in the Digital Space
Onwards to 100
We’ve all felt the sting of receiving an undeserved C, or even dropping from an A to a D. It’s disheartening and can sap our motivation. Traditional grading operates on the premise of starting with a perfect 100% score and deducting points for mistakes. In contrast, gameful learning principles advocate for a fresh start, earning points for each task completed successfully. This approach emphasizes positive feedback, which in turn boosts motivation.
The Option to Choose
As the Self-determination Theory states, offering choices enhances the learning journey and fosters intrinsic motivation. Yet, striking a balance is crucial here: an excess of choices can overwhelm learners. It’s advisable to gradually empower learners with autonomy throughout the learning process. For instance, providing diverse pathways to complete a course can cater to various learning preferences. This might include options like videos, interactive exercises, downloadable materials, and more.
Immediate Feedback, Visible Progress
Playing games often creates a sense of time slipping away, immersing us entirely in the game world, free from external distractions. This captivating experience is often achieved through immediate feedback to our actions. In e-learning, replicating this dynamic is possible through features like automatic quizzes, frequent feedback from virtual characters or peers, and guidance from instructors. These mechanisms allow learners to witness the direct impact of their actions, enabling tangible progress in the learning journey.
The Freedom to Fail
Numerous games build on the concept of learning from failures. When we encounter setbacks, we adapt our strategies until we succeed. Similarly, courses and learning materials designed with playful learning principles encourage experimentation and trial and error. Features such as quiz retakes provide ample opportunities for learners to step out of their comfort zones, fostering the acquisition of new skills.
“Glass-Course”
Just like with e-learning platforms, creating a user-friendly learning environment is paramount for effective education. In materials designed around playful learning principles, transparency is key and typically consists of three main elements:
- Clearly define the criteria for course completion from the start.
- Maintain consistency in the scoring system throughout the learning journey.
- Provide clear instructions for completing sub-tasks and assignments.
Competition and Cooperation
When we unite in teams against the “machine,” each member holds a crucial role, fostering easier bonding. However, in competitive scenarios where teams face off, it’s vital to ensure that even the losing side, such as the last-place team, can earn points through individual tasks and receive positive feedback. This inclusion promotes a sense of participation and encouragement for all participants, regardless of team performance.

The Curriculum Development Process
Curious about the production of teaching materials? A product of our research, the five-cycle model, is based on alternating creative and research processes and continuous feedback.
Read more!Who Are We?
We are digital education experts and software developers, following trends and offering innovative solutions in our learning materials and systems. We have been providing digital training, creating complex e-learning materials and implementing systems for X years.
Klippe Learning’s team will create the digital teaching and learning solution you’ve been dreaming of – or we’ll dream it for you if you don’t know exactly what you need. Custom content, creative and motivating methods, a platform tailored to you.
How Can You Reach Us?
To find out more about our bespoke learning materials, e-learning systems, training courses or to request a quote, please contact us:
 contact us via the form on the right!
contact us via the form on the right!
 or call us:
or call us:
 or send an email:
or send an email:



